- Home
- Hydronic radiant floor heating
- Hydronic Baseboard Heating
Are Hydronic Baseboard Heating Systems Worth the Money? Advantages and Disadvantages
Is the hydronic baseboard heating system the right solution for your home? How does the hot water baseboard heater work, what are the advantages, disadvantages, and types? Can we combine baseboard heating with the existing radiant floor heating or any other system?
Installing hydronic baseboard heating? This is what you should consider.
- How does the hydronic baseboard heating work?
- Types
- One-pipe vs. series-loop systems
- Sizing tips
- Installing tips
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Radiant floor heating vs. baseboard heating
How does the hydronic baseboard heating work?
Hydronic baseboard heating systems are systems used for the whole-house heating utilizing a boiler or furnace to heat the water, pumps to transfer the hot water through the pipes, and baseboard heaters to heat the air. These heaters, also known as panels, radiators, or convectors, are installed in each room of the house, and from there, in the form of radiant heat and convection, they transfer the heat to the surrounding air.
Hot water baseboard heaters are an excellent alternative for your home heating and can be used to support an existing HVAC system.
The heat that the baseboard convector releases warms up the adjacent walls and surrounding air from the bottom up. As the room air gets cooled, it moves down and inside the heaters, where it gets heated again.
Baseboard heating is just one type of hydronic home heating systems, and as the popular radiator system, it uses many elements to make it safe and functional.
Cold and hot water smoothly circulates through the system by using the pumps, and for the temperature and pressure control, elements such as the expansion tank, zone valves, relief valves, and thermostats are used, making the heating system safe, reliable, and efficient.
Types
There are two types of baseboard heaters: electric and hydronic.
The electric type uses electricity to heat the air directly or heat the fluid inside the heater, where each unit can be connected to its own thermostat so each room's temperature can be set independently.
The hydronic heaters are part of the central system, so within each water is heated with any of the popular fuels: gas, oil, electricity, or solar, where water is centrally heated either inside the boiler, tank-type, or tankless water heater, or heated locally inside the unit.
Baseboard water heaters are made of tubes or channels so hot water can circulate through and radiate the heat into the room. They are hollow or finned units that heat well-insulated rooms uniformly with a little temperature difference between the ceiling and floor.
Baseboard panels are usually designed with fins to increase the heating area to emit more heat and make it more efficient.
Some systems have thermostatically controlled electric heaters installed in the hydronic baseboard heaters, submerged in the heat transfer fluid, so the central boiler is not needed.
One-pipe vs. series-loop systems
Two of the most used and popular hot water systems are the one-pipe system and series-loop systems; both operated using either forced or gravity circulation.
One-pipe systems have the advantage of shutting off two baseboard heating panels without disturbing hot water flow to other units.
Series-loop heating systems are more straightforward and cost-effective solution, where panels are connected in series, forming a supply line.
Hydronic heating can be used for different applications such as preparing domestic hot water for residential use, hot water for swimming pools, snow melting, and radiant floor heating. Every application has an independent circuit controlled by its thermostats while getting hot water from the primary circuit.
With today's trend of going green, geothermal heating and cooling are also becoming interesting and more popular.
Sizing tips
To provide a sufficient amount of heat for each room, each baseboard heater has to be sized correctly.
If you choose a heater that is too small, the comfort will be affected (reduced) as the desired temperate set on the thermostat probably won't be met, and the heater would work non-stop, which will reduce the unit's lifespan and increase the energy use.
If you choose an oversized heater, the unit will run frequently and in short cycles, also reducing the lifespan, increasing the energy and heating costs.
So, here are a few tips on how to size a hydronic baseboard heater properly, and calculate the heating requirements (output in BTU) for each room:
- Measure the area of each room you want to heat.
- Use the formula: A=L x W (area=length x width).
- Find out the climate zone based on the home location (use this link with a climate zone map) and determine the heating factor.
- Calculate the BTU requirements for each room. For example, for the well-insulated house in Zone 1, use the heating factor of 30 BTU.
- Use the formula to get the power output: A x 30 BTU (area x 30 BTU).
- Take into account the energy efficiency because the BTU that you will calculate using the above formula does not include the energy loss. If the efficiency is 90%, for example, 10% is a loss.
- Take the power output you calculated in step 3 and divide it by the efficiency.
Example:
Room area - 400 sq.ft
Heating factor – 30
Efficiency 90% (90/100=0.9)
Formula: 400 x 30 /0.9= 13,333 BTU
Or use the calculator as found on this site.
Installing tips
To find the best location for your baseboard panels so they can heat the room efficiently and fast, it is crucial to know how they work.
As said before, baseboard heating systems work through convection. The cold air from the walls/windows is heavier than hot air, so it naturally falls and then enters the baseboard unit, where it gets heated and moving upwards.
So, as the cold air falls and heat air rises, this forces the air to circulate inside the room, warming up the whole room while blocking the drafts and cold.
The best location for installing the baseboard panels is on the external wall, the outer perimeter of the home, below the windows, and at the baseboard level of your home.
Sometimes, these panels are enclosed in a cabinet - for the appearance, with the opening at the bottom and top for the air transfer.
Installing electric baseboard heaters is much easier than the central HVAC system with all the plumbing and soldering work involved. They have to be plugged into the standard household electric outlet.
Electric baseboard heaters are very economical and safe; and can be used as a room-by-room solution. There are freestanding and movable heaters that do not require any installation and other mountable or wall models.
Properly installed baseboard heaters are mounted at least one inch above the finished floor, allowing the free flow of the air through the heater and further into the room.
Advantages of hydronic vs. forced-air systems
Hydronic baseboard heating systems provide an efficient way to heat your home; they work quietly and accurately with the system of controls such as valves and thermostats. They are flexible. They can be used in combination with radiant floor heating, and the perfect time is when retrofitting and remodeling your home.
They offer comfort, and since they are working with lower temperatures, they provide a cost-effective solution. The result is draft-free heating, the heat is cleaner and healthier, and it does not irritate your throat with burnt dust particles.
It is easier to zone such systems than forced air systems so that you can control the heat in each room.
It is quiet as there are no noisy air ducts and blowers.
The reason for the higher efficiency is because it takes heated water longer to cool than the forced-air system.
Disadvantages
Hydronic systems are generally more expensive than other types.
Dust is a problem with forced-air heating systems but is not a big issue with hydronic baseboard heat. Unfortunately, dust still gets into the fins and from there into the room air.
They occupy wall space, so the arrangement of your furniture greatly depends on the location of these heaters. If hiding the baseboard heater with the furniture, you will block the proper heat distribution, and the efficiency will be reduced.
As opposed to the forced-air systems, baseboard heating provides a slow temperature increase, so it takes longer to warm up the room. This is especially a problem in places with freezing temperatures, in a case where the vacation home is left unheated. The system has to be drained or, even better, filled with propylene glycol to prevent freezing.
Baseboard heating vs. radiant floor heating
When comparing baseboard vs. radiant floor heating, they work the same, but the initial cost for baseboard heating is lower. While baseboard heaters occupy the room space, they don't require tearing up the flooring, such as when installing radiant floor heating systems.
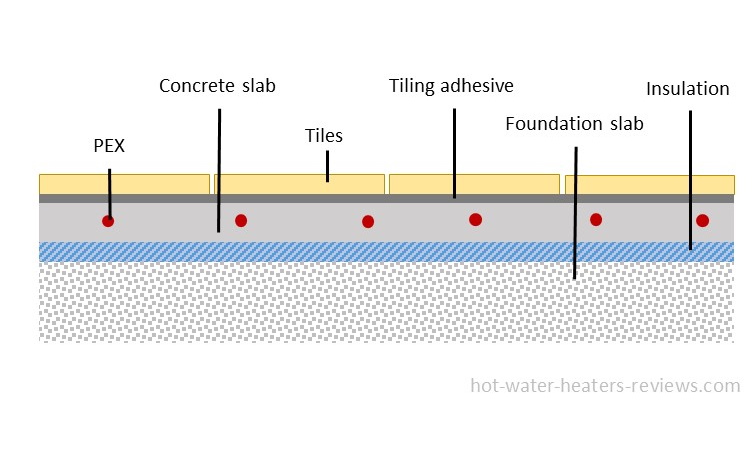
In hydronic baseboard heating, the boiler produces hot water with a higher temperature, which requires copper tubing for hot water transfer. The most common size for copper tubing used here is either 1/2 or 3/4". In radiant floor heating, cheaper PEX pipes are used because these are working with the lower operating temperature.
Summary
Hydronic baseboard heating is very effective way of heating, so they are mainly used in colder areas such as northern states in the US and Canada. Either you are building a new home, remodeling, or planning to retrofit your home heating, hot water baseboard heat can be combined with radiant floor heating.
When buying a baseboard panel, look for the proper size heater based on the room size and calculations. Also, get the complete assembly, where the pipe and heating fins are inside the case.
- Home
- Hydronic radiant floor heating
- Hydronic Baseboard Heating